Echelon Biosciences, Inc (EBI) products
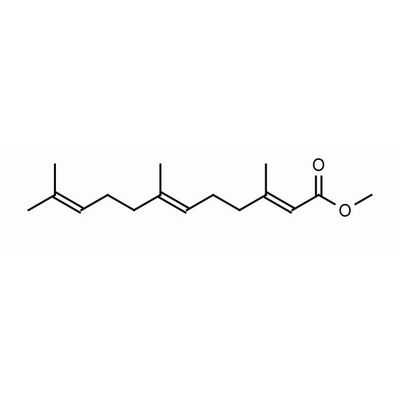
(E,E)-Methyl Farnesoate
Methyl farnesoate (MF) is a crustacean reproductive hormone that is structurally similar to insect juvenile hormone. It is responsible for enhancing reproductive maturation, maintaining juvenile morphology, and influencing male sex determination. Exposure of female Daphnids to increasing levels of MF increases the percentage of males in a brood in a dose-dependant manner. MF is endogenously produced in the mandibular organ and environmental factors such as salinity and temperature can influence hemolyph levels.
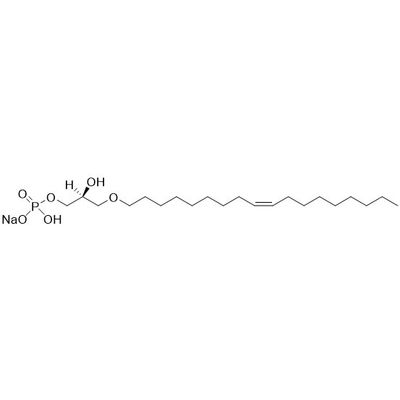
(2S)-Oleyl LPA
(2S)-Oleyl LPA is an analog of 18:1 LPA in which the fatty ester bond to gycerol has been replaced by a metabolically stable ether linkage. Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA) is a small lysophospholipid involved in diverse cellular processes such as cell proliferation, chemotaxis, platelet aggregation, wound healing, angiogenesis, tumor invasion, and smooth muscle contraction. LPA binds to several G-coupled protein receptors to initiate its biological functions. In cancer, LPA primarily promotes cell survival, migration and invasion.
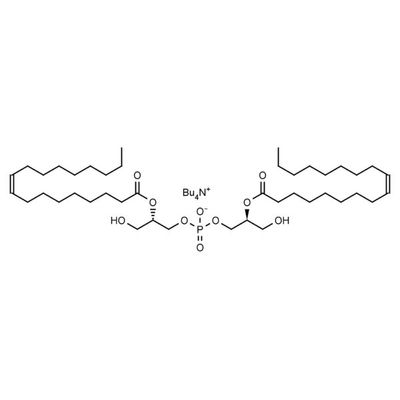
(S,S) Bisoleoyl-Lysobisphosphatidic Acid (LBPA)
Lysobisphosphatidic acids (LBPAs), known also as bis-(monoacylglycerol)phosphates (BMPs) are specialized lipids reported to play a role in intracellular protein and lipid transport in healthy cells. Their accumulation was observed in pathologic liver tissue, and they also serve as antigens for auto-antibody generation in a human autoimmune condition termed antiphospholipid syndrome. Accumulation of LBPAs in intracellular, often multilamellar membranes is related to biomembrane polymorphism which may impact intracellular cholesterol transport. (S,S) Bisoleoyl-lysobisphosphatidic acid is the naturally occurring, biologically active isomer of LPBA.
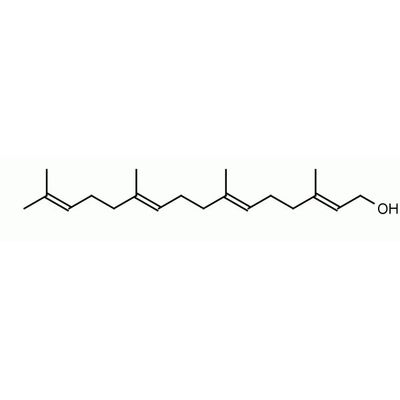
(E,E,E)-Geranylgeraniol
(E,E,E)-Geranylgeraniol is an intermediate in the biosynthetic pathway of vitamins E & K and is linked to proteins via post-translational modification.
Antibodies & Proteins
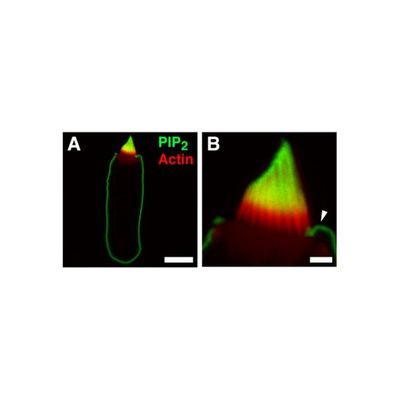
Anti-PtdIns (4,5) P2 IgM In Ascites
Phosphoinositides (PIPns) are minor components of cellular membranes but are integral signaling molecules for cellular communication. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) has been shown to play a central role in a variety of cellular functions. Amongst its many functions, PIP2 is a substrate for Phospholipase C-coupled G-protein pathways involved in intracellular calcium release in a number of tissues. It is also a substrate for class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3-K) forming PIP3.