Refine by
Particle Sizing Articles & Analysis
46 articles found
Hello, and welcome back to the Colorful Researcher’s blog. In our last blog, Peter discussed how AI is accelerating the drug discovery process and putting pressure on chemists, who must find ways of developing these potential drugs for subsequent testing or production. In his post, Peter explained how small instruments like BUCHI’s Glass Oven G-300 are great for working with small ...
ByBUCHI
What are Dyed Polystyrene Latex Particles? Polystyrene particles (PSP) are commercially available in different sizes, ranging from 15 nanometers to several micrometers, with narrow size distributions and various surface chemistries. Additionally, polystyrene is generally considered inert and nontoxic, making it safe for use in a variety of biological assays. Dyed polystyrene latex particles or ...
Hydroxyapatite (HA), a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite, has emerged as a cornerstone material in modern science and technology. Its unique properties, such as biocompatibility, bioactivity, and structural similarity to human bone and teeth, make it indispensable in fields like biomedical engineering, environmental science, and advanced materials. This article delves into the ...
ByMatexcel
Evaluating the thermal stability of collagen is a crucial step in understanding its physical and chemical properties and assessing its potential applications. Thermal stability generally refers to the ability of collagen to maintain its structure and function during the heating process. Here are some common methods to evaluate the thermal stability of collagen:1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry ...
The determination of collagen molecular weight is a technique used to determine the molecular weight of collagen, a complex protein. Collagen is one of the richest proteins in animals, mainly found in the skin, bones, tendons and connective tissue. Due to its key role in cell structure and tissue regeneration, accurate determination of the molecular weight of collagen is of great significance to ...
The field of pharmaceuticals has seen rapid advancements in drug delivery technologies in recent years, one of which is long-lasting controlled-release microspheres technology. This technology involves the use of microscopic particles to deliver drugs in a controlled and sustained manner over an extended period of time. By encapsulating drugs within these microspheres, pharmaceutical companies ...
POCT (Point-of-Care Testing) refers to clinical and bedside testing conducted in close proximity to patients. It is often not performed by clinical laboratory personnel. POCT holds significant importance in disease prevention, etiology determination, prognosis, enhancing treatment outcomes, and reducing healthcare expenses. It meets clinical testing needs across various healthcare settings. POCT ...
Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) is a functional polymer organic compound randomly polymerized by lactic acid (PLA) and glycolic acid (PGA). It has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration It is certified by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and is a copolymer material available on the market. PLGA has good biocompatibility, biodegradability, mechanical strength, good ...
What are Adjuvants? Adjuvants, also known as immunomodulators or immune enhancers, are an additive to vaccines. Adjuvants are non-specific immune enhancers that enhance or alter the type of immune response to an antigen. Adjuvants can help antigens induce long-term effective specific immune responses in vivo, leading to higher vaccine efficacy and prolonged protection from immune responses. ...
siRNA, with a molecular weight of about 13 kDa, recruits the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to mRNA through base pairing, thereby inhibiting protein translation. The mRNA is targeted for cleavage through the catalysis of the RISC protein Ago2, a member of the Argonaute family. In addition, other Ago proteins (Ago1, Ago3, and Ago4) catalyze endonuclease-mediated degradation of non-specific ...
Nano-flow cytometry is a revolutionary technology that has the potential to transform early disease detection and diagnosis. Nano-flow cytometers are able to detect and analyze individual nanoparticles, including extracellular vesicles and viruses, with high sensitivity and accuracy. This makes them ideal for detecting diseases at their earliest stages, when they are most treatable. How does ...
Microencapsulation technology has revolutionized drug delivery systems, allowing for the protection and controlled release of therapeutic agents. Microcapsules, tiny spherical structures capable of encapsulating drugs, offer numerous advantages in terms of stability, targeted delivery, and improved patient outcomes. In this article, we will delve into the methods involved in preparing drug ...
Microspheres are small spherical entities formed by dispersing or adsorbing drugs in a polymer matrix. The particle size is typically between 1 μm and 250 μm, and the largest can reach more than 800 μm. Microsphere technology is at the intersection of cutting-edge disciplines such as materials science, polymer technology, medical technology, and microelectronics. Once injected into the ...
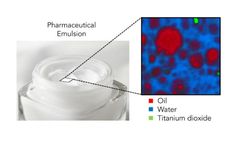
Welcome to Edinburgh Instruments’ monthly blog celebrating our work in Raman, Photoluminescence, and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging. Every month we will highlight our pick for Map of the Month to show how our spectrometers can be used to reveal all the hidden secrets in your samples.JuneAn emulsion can be defined as a mixture in which a liquid, such as oil, is dispersed in small globules through ...
Chitin is the second largest natural polymer after cellulose, and it exists widely in nature, such as shells of crustaceans such as shrimps, crabs, insects, and cell walls of fungi. Although chitin has good biocompatibility and biodegradability, its poor solubility limits its practicality in the field of biomedicine. The product of chitin deacetylation is chitosan. Chitosan is structurally ...
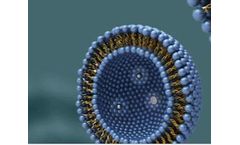
Liposomes are a novel drug delivery system (DDS). They are bimolecular vesicles that form spontaneously when phospholipids are dispersed in water. Liposomes vary in size, composition and charge and can be used as carriers for a wide range of drug molecules, such as chemotherapeutic agents, antimicrobial and antiviral drugs, antiparasitic drugs, genetic material, vaccines, therapeutic proteins, ...
Due to the amphiphilic nature of lipids in liposomes, they can serve as candidate vehicles for drug delivery, and liposomes have received more attention than other systems because of their remarkable ability to deliver drugs to their target sites. Advantages of Liposomes as Drug Delivery Vehicles l As drug delivery vehicles, liposomes have low toxicity and immunogenicity, and the high ...
Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular intake and uptake of molecules ranging from nano-size particles to small chemical compounds to large fragments of DNA. As a versatile peptide, CPP has been widely used for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. 1. Oligo and siRNA Transport As an important means for targeted therapy of specific genes, oligonucleotides ...
Following the coronavirus emergency, surgeries and medical offices shall be reorganised to work safely. One of the first safety measure to adopt concerns suction of aerosol potentially infected. ...
ByAirsafe
Sucrose is a disaccharide with a unique structure. It is a non-reducing sugar formed by removing a molecule of water from the glycoside hydroxyl group of a molecule of α-D-(+)-glucopyranose and a molecule of β-D-(-)-fructofuranose. During the hydrolysis process, the specific optical rotation of sucrose gradually changes from dextrorotatory to levorotatory, so the hydrolysis of sucrose ...